 Ransomware is on the rise and is going after more victims with little to no defenses, small to medium-small sized businesses and even quiet non-profits. Here are a few tools with a valid track record of stopping and removing 3 common types of ransomware.
Ransomware is on the rise and is going after more victims with little to no defenses, small to medium-small sized businesses and even quiet non-profits. Here are a few tools with a valid track record of stopping and removing 3 common types of ransomware.
1) LockCrypt is a ransomware discovered in June 2017 but is still active in various mutations. It spreads by brute forcing Remote Desktop Protocol credentials – a key port (3389) that should be obviously locked. A prominent example of this exploit occurred in December 2017 when an employee opened an email which was maliciously sent from another co-worker’s account. This was merely an attempt to trick the person to click on the malicious attachment which was appended to the letter. Once it was opened, the ransomware download began after which 48 out of 500 servers of North Carolina County were compromised with LockCrypt (Ugnius Kiguolis, Spyware.com, 12/11/17).
As per Bitdefender, this ransomware family has several sub-variants with the following specific extensions, the first (.1btc) is decryptable with this free Bitdefender tool and the others may be decryptable with the free Trend Micro Malwarebytes Ransomware File Decryptor tool (check for updates).
- .1btc (decryptable and included in this version of the tool)
- .lock (decryptable, not included in our tool)
- .2018 (decryptable, not included in our tool)
- .bi_d (not decryptable)
- .mich (decryptable, not included in our tool)
2) The five-year-old ransomware Trojan-Ransom.Win32.Rakhni has received a facelift recently which now allows it to decide whether or not to install its traditional ransomware or to drop a cryptominer.
The malware is delivered through spam campaigns where the email comes with a PDF attached which the receiver is prompted to save and then enable editing. When the victim attempts to open the document he or she is presented with an executable that portrays itself as an Adobe Reader plugin and it asks the person to allow it to make changes to their computer (Doug Olenick, SC Magazine, 07/06/18).
According the Kaspersky labs, the current injection chain on this newer exploit is largely the same as before. However, the malware moves along a rather complex path before it decides which form it will take. During the process it will check to make sure the device is not a virtual machine, it will check for and disarm an AV software and also Widows Defender and finally erase most of the footprints made during the malware installation.
The executable, which is written in Delphi and has its strings encrypted, then presents a message box that states the PDF could not be opened, basically to keep the victim from thinking anything negative is about to happen (Doug Olenick, SC Magazine, 07/06/18).
It first checks that the device has one of the substrings:
- \TEMP
- \TMP
- \STARTUP
- \CONTENT.IE
- Registry check
It then checks to see if the registry contains checks that in the registry there is no value HKCU\Software\Adobe\DAVersion and if it finds this is so it creates HKCU\Software\Adobe\DAVersion = True (Doug Olenick, SC Magazine, 07/06/18). As of Feb 2018 Kaspersky Labs has a free decryption tool (since updated) to get rid of most variations of this infection.
3) Thousands of LabCorp’s servers were impacted by the SamSam ransomware attack on 07/13/18, a CSO online report confirmed (Steve Ragan, 07/19/18). Early information indicates that the company contained the spread of the infection and neutralized the attack within 50 minutes – great. However, before the attack was fully contained, 7,000 systems and 1,900 servers were negatively impacted; 350 were production servers (Steve Ragan, CSO Online, 07/19/18. This is a growing trend in the healthcare sector that reached 15% in 2016 (Fig1. Greg Slabodkin, Health Data Management, 04/11/18).
Fig. 1.
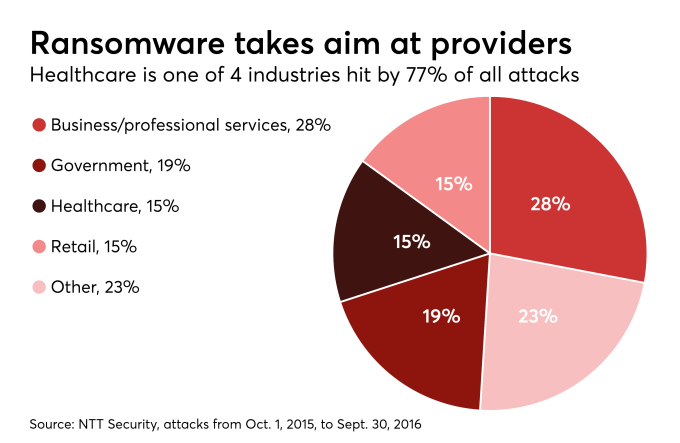 As per Jessica Davis of HealthcareITnews, “SamSam is the virus that shut down the Allscripts platform for about a week in January 2017 and is known to use brute force RDP (remote desktop protocol) attacks to breach a system and spread. The variant is also responsible for taking down Hancock Health, Adams Memorial and the government systems of Atlanta — among a host of others” (HealthcareITNews.com, 07/20/18).
As per Jessica Davis of HealthcareITnews, “SamSam is the virus that shut down the Allscripts platform for about a week in January 2017 and is known to use brute force RDP (remote desktop protocol) attacks to breach a system and spread. The variant is also responsible for taking down Hancock Health, Adams Memorial and the government systems of Atlanta — among a host of others” (HealthcareITNews.com, 07/20/18).
The ransom note it displays is quite interesting, giving the option of randomly-selected file encryption (if you don’t pay the full amount). They’ll also unlock one file for free as a token of trust that they will give your files back after payment (Christopher Boyd, Malwarebytes Labs, 05/01/18).
Fig. 2. (Barkly Blog, Jonathan Crowe, Jan 2018).
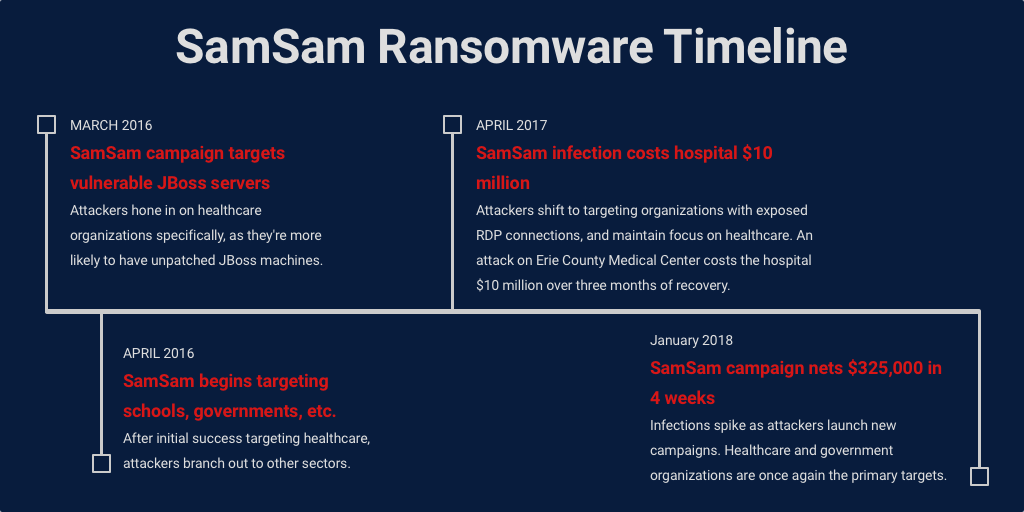 The virus has been updated a couple of times. Currently, it appends one of the following file extensions (Julie Splinters, spyware.com, 06/23/18):
The virus has been updated a couple of times. Currently, it appends one of the following file extensions (Julie Splinters, spyware.com, 06/23/18):
- .weapologize;
- .AreYouLoveMyRansFile;
- .breeding123;
- .country82000;
- .disposed2017;
- .fucku;
- .happenencedfiles;
- .helpmeencedfiles;
- .howcanihelpusir;
- .iaufkakfhsaraf;
- .mention9823;
- .myransext2017;
- .noproblemwedecfiles;
- .notfoundrans;
- .prosperous666;
- .powerfulldecryp;
- .supported2017;
- .suppose666;
- .VforVendetta
- .Whereisyourfiles;
- .wowreadfordecryp;
- .wowwhereismyfiles;
- .loveransisgood.
Different variants of the virus might drop different versions of ransom notes. However, at the moment victims might receive one of these ransom notes in:
- 0009-SORRY-FOR-FILES.html,
- IF_WANT_FILES_BACK_PLS_READ.html,
- 000-PLEASE-READ-WE-HELP.html,
- 000-No-PROBLEM-WE-DEC-FILES.html,
- READ-FOR-DECCCC-FILESSS.html,
- HELP_DECRYPT_YOUR_FILES.HTML,
- 001-HELP_FOR_DECRYPT_FILE.html,
- 006-READ-FOR-HELLPP.html,
- PLEASE_READ_FOR_DECRYPT_FILES_[Number].html,
- PLEASE-README -AFFECTED-FILES.html.
SamSam is the newest and most powerful of the three types of ransomeware mentioned above. There is no known decryption tool or fix for data that you don’t already have your data backed up. Yet it is known to uses tools such as Mimikatz to steal valid user credentials and common IT management tools to move malware to new hosts. Attackers and their malware are increasingly reliant on Mimikatz and similar tools, such as PsExec — associated with everything from PoS malware to webshells — to spread through the network and do damage (Dark Reading, 06/20/18, Ajit Sancheti). Stay tuned here for updates regarding a stable decryption tool for SamSam.
