Minneapolis — 01/08/22
Intro:
Every year I like to research and commentate on the most impactful security technology and business happenings from the prior year. This year is unique since the pandemic and mass resignation/gig economy continues to be a large part of the catalyst for most of these trends. All these trends are likely to significantly impact small businesses, government, education, high tech, and large enterprise in big and small ways.

Summary:
The pandemic continues to be a big part of the catalyst for digital transformation in tech automation, identity and access management (IAM), big data, collaboration tools, artificial intelligence (AI), and increasingly the supply chain. Disinformation efforts morphed and grew last year challenging data and culture. This requires us to put more attention on knowing and monitoring our own social media baselines. We no longer have the same office due to mass work from home (WFH) and the mass resignation/gig economy. This infers increased automated zero-trust policies and tools for IAM with less physical badge access required. The security perimeter is now more defined by data analytics than physical/digital boundaries.
The importance of supply chain cyber security was elevated by the Biden Administration’s Executive Order 1407 in response to hacks including SolarWinds and Colonial Pipeline. Education and awareness around the review and removal of non-essential mobile apps grows as a top priority as mobile apps multiply. All the while, data breaches, and ransomware reach an all-time high while costing more to mitigate.
1) Disinformation Efforts Accelerate Challenging Data and Culture:
Disinformation has not slowed down any in 2021 due to sustained advancements in communications technologies, the growth of large social media networks, and the “appification” of everything thereby increasing the ease and capability of disinformation. Disinformation is defined as incorrect information intended to mislead or disrupt, especially propaganda issued by a government organization to a rival power or the media. For example, governments creating digital hate mobs to smear key activists or journalists, suppress dissent, undermine political opponents, spread lies, and control public opinion (Shelly Banjo; Bloomberg, 05/18/2019).
Today’s disinformation war is largely digital via platforms like Facebook, Twitter, Instagram, Reddit, WhatsApp, Yelp, Tik-tok, SMS text messages, and many other lesser-known apps. Yet even state-sponsored and private news organizations are increasingly the weapon of choice, creating a false sense of validity. Undeniably, the battlefield is wherever many followers reside.
Bots and botnets are often behind the spread of disinformation, complicating efforts to trace and stop it. Further complicating this phenomenon is the number of app-to-app permissions. For example, the CNN and Twitter apps having permission to post to Facebook and then Facebook having permission to post to WordPress and then WordPress posting to Reddit, or any combination like this. Not only does this make it hard to identify the chain of custody and original source, but it also weakens privacy and security due to the many authentication permissions involved. The copied data is duplicated at each of these layers which is an additional consideration.
We all know that false news spreads faster than real news most of the time, largely because it is sensationalized. Since most disinformation draws in viewers which drives clicks and ad revenues; it is a money-making machine. If you can significantly control what’s trending in the news and/or social media, it impacts how many people will believe it. This in turn impacts how many people will act on that belief, good or bad. This is exacerbated when combined with human bias or irrational emotion. For example, in late 2021 there were many cases of fake COVID-19 vaccines being offered in response to human fear (FDA; 09/28/2021). This negatively impacts culture by setting a misguided example of what is acceptable.
There were several widely reported cases of political disinformation in 2021 including misleading texts, e-mails, mailers, Facebook censorship, and robocalls designed to confuse American voters amid the already stressful pandemic. Like a narcissist’s triangulation trap, these disinformation bursts riled political opponents on both sides in all states creating miscommunication, ad hominin attacks, and even derailed careers with impacts into the future (PBS; The Hinkley Report, 11/24/20 and Daniel Funke; USA Today, 12/23/21).
Facebook is significantly involved in disinformation as one recent study stated, “Globally, Facebook made the wrong decision for 83 percent of those ads that had not been declared as political by their advertisers and that Facebook or the researchers deemed political. Facebook both overcounted and undercounted political ads in this group” (New York University; Cybersecurity For Democracy, 2021). Of course, Facebook disinformation whistleblower Frances Haugen who testified before Congress in 2021 is only more evidence of these and related Facebook failings. Specifically that “Facebook executives, including CEO Mark Zuckerberg, misstated and omitted key details about what was known about Facebook and Instagram’s ability to cause harm” (Bobby Allyn; NPR, 10/05/21).
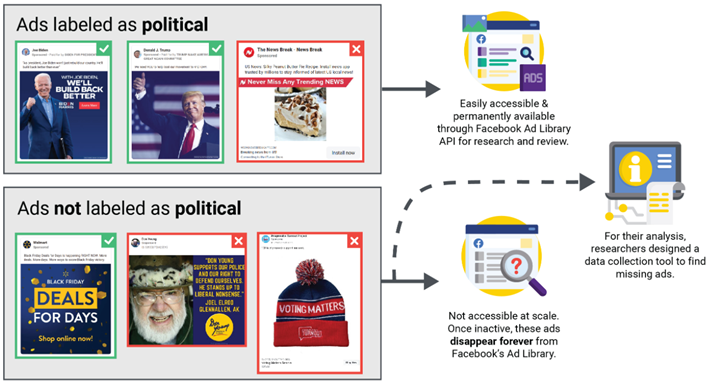
With the help of Facebook’s misinformation, huge swaths of confused voters and activists aligned more with speculation and emotion/hype than unbiased facts, and/or project themselves as fake commentators. This dirtied the data in terms of the election process and only begs the question – which parts of the election information process are broken? This normalizes petty policy fights, emotional reasoning, lack of unbiased intellectualism – negatively impacting western culture. All to the threat actor’s delight. Increased public to private partnerships, more educational rigor, and enhanced privacy protections for election and voter data are needed to combat this disinformation.
2) Identity and Access Management (IAM) Scrutiny Drives Zero Trust Orchestration:
The pandemic and mass resignation/gig economy has pushed most organizations to amass work from home (WFH) posture. Generally, this improves productivity making it likely to become the new norm. Albeit with new rules and controls. To support this, 51% of business leaders started speeding up the deployment of zero trust capabilities in 2020 (Andrew Conway; Microsoft, 08/19/20) and there is no evidence to suggest this is slowing down in the next year but rather it is likely increasing to support zero trust orchestration. Orchestration is enhanced automation between partner zero trust applications and data, while leaving next to no blind spots. This reduces risk and increases visibility and infrastructure control in an agile way. The quantified benefit of deploying mature zero trust capabilities including orchestration is on average $ 1.76 million dollars less in breach response costs when compared to an organization who has not rolled out zero trust capabilities (IBM Security, Cost of A Data Breach Report, 2021).
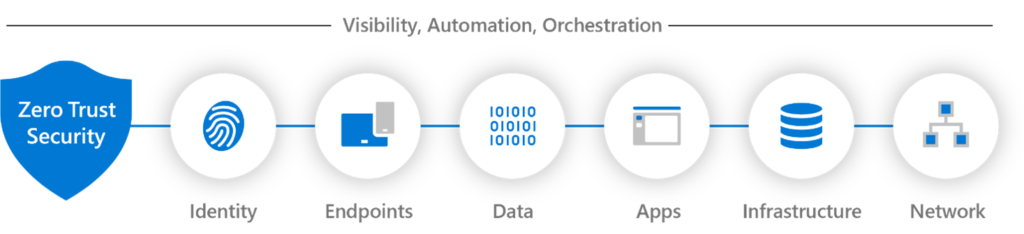
Zero trust moves organizations to a need-to-know-only access mindset with inherent deny rules, all the while assuming you are compromised. This infers single sign-on at the personal device level and improved multifactor authentication. It also infers better role-based access controls (RBAC), firewalled networks, improved need-to-know policies, effective whitelisting and blacking listing of apps, group membership reviews, and state of the art PAM (privileged access management) tools for the next year. In the future more of this is likely to better automate and orchestrate (Fig. 3.) zero trust abilities so that one part does not hinder another part via complexity fog.
3) Security Perimeter is Now More Defined by Data Analytics than Physical/Digital Boundaries:
This increased WFH posture blurs the security perimeter physically and digitally. New IP addresses, internet volume, routing, geolocation, and virtual machines (VMs) exacerbate this blur. This raises the criticality of good data analytics and dashboarding to define the digital boundaries in real-time. Therefore, prior audits, security controls, and policies may be ineffective. For instance, empty corporate offices are the physical byproduct of mass WFH, requiring organizations to set default disable for badge access. Extra security in or near server rooms is also required. The pandemic has also made vendor interactions more digital, so digital vendor connection points should be reduced and monitored in real-time, and the related exception policies should be re-evaluated.
New data lakes and machine learning informed patterns can better define security perimeter baselines. One example of this includes knowing what percent of your remote workforce is on what internet providers and what type? For example, Google fiber, Comcast cable, CenturyLink DSL, ATT 5G, etc. There are only certain modems that can go with each of these networks and that leaves a data trail. Of course, it could be any type of router. What type of device do they connect with MAC, Apple, VM, or other, and if it is healthy can all be determined in relationship to security perimeter analytics.
4) Supply Chain Risk and Attacks Increase Prompting Government Action:
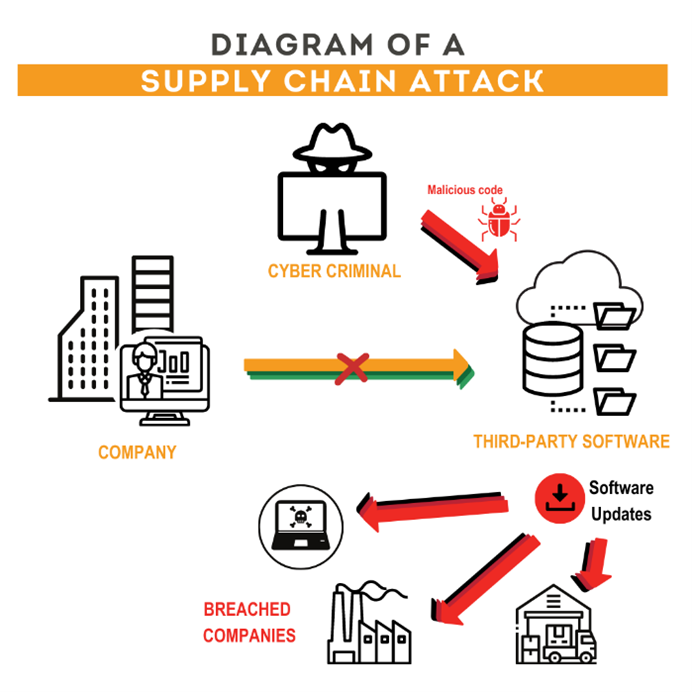
Every organization has a supply chain big or small. There are even subcomponents of the supply chain that can be hard to see like third/fourth-party vendors. A supply chain attack works by targeting a third/fourth party with access to an organization’s systems instead of hacking their networks directly.
In 2021 cybercriminals focused their surveillance on key components of the supply chain including hacking DNS servers, switches, routers, VPN concentrators and services, and other supply chain connected components at the vendor level. Of note was the massive Colonial Gas Pipeline hack that spiked fuel prices this last summer. This was caused by one compromised VPN account informed by a leaked password from the dark web (Turton, William; and Mehrotra, Kartikay; Bloomberg, 06/04/21). The SolarWinds hack was another supply chain-originated attack in that they got into SolarWinds IT management product Orien which in turn got them into the networks of most of the customers of that product (Lily Hay Newman; Wired, 12/19/21). The research consensus unsurprisingly ties this attack to Russian affiliated threat actors and there is no evidence contracting that.
In response to these and related attacks the U.S. Presidential Administration issued Executive Order 14017, the heart of which requires those who manufacture and distribute software a new awareness of their supply chain to include what is in their products, even open-source software (White House; 05/12/21). This in addition to more spending on CISA hiring and public relations efforts for vulnerabilities and NIST framework conformance. Time will tell what this order delivers as it is dependent on what private sector players do.
5) Data Breaches Have Greatly Increased in Number and Cost:
The pandemic has continued to be a part of the catalyst for increased lawlessness including fraud, ransomware, data theft, and other types of profitable hacking. Cybercriminals are more aggressively taking advantage of geopolitical conflict and legal standing gaps. For example, almost all hacking operations are in countries that do not have friendly geopolitical relations with the United States or its allies – and all their many proxy hops would stay consistent with this. These proxy hops are how they hide their true location and identity.
Moreover, with local police departments extremely overworked and understaffed with their number one priority being responding to the huge uptick in violent crime in most major cities, white-collar cybercrimes remain a low priority. Additionally, local police departments have few cyber response capabilities depending on the size of their precinct. Often, they must sheepishly defer to the FBI, CISA, and the Secret Service, or their delegates for help. Yet not unsurprisingly, there is a backlog for that as well with preference going to large companies of national concern that fall clearly into one of the 16 critical infrastructures. That is if turf fights and bureaucratic roadblocks don’t make things worse. Thus, many mid and small-sized businesses are left in the cold to fend for themselves which often results in them paying ransomware, and then being a victim a second time all the while their insurance carrier drops them.
Further complicating this is lack of clarity on data breach and business interruption insurance coverage and terms. Keep in mind most general business liability insurance policies and terms were drafted before hacking was invented so they are by default behind the technology. Most often general liability business insurance covers bodily injuries and property damage resulting from your products, services, or operations. Please see my related article 10 Things IT Executives Must Know About Cyber Insurance to understand incident response and to reduce the risk of inadequate coverage and/or claims denials.
According to the Identity Theft Resource Center (ITRC)’s 2021Q3 Data Breach Report, there was a 17% year-over increase as of 09/30/21. This means that by the time they finish their Q4 2021 report it’s likely to be above a 30% year-over-year increase. Breaches are also more costly for organizations suffering them according to the IBM Security Cost of Data Breach Report (Fig 5).
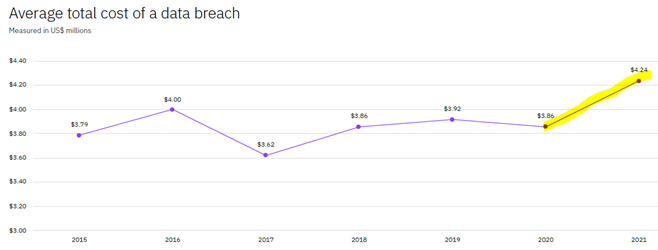
From 2020 to 2021 the average cost of a data breach in U.S. dollars rose to $4.24 million from $3.86 million. This is almost a 10% increase at 9.1%. In contrast, the preceding 4 years were relatively flat (Fig 5). The pandemic and policing conundrum is a considerable part of this uptick.
Lastly, this is a lot of money for an organization to spend on a breach. Yet this amount could be higher when you factor in other long-term consequence costs such as increased risk of a second breach, brand damage, and/or delayed regulatory penalties that were below the surface – all of which differs by industry. In sum, it is cheaper and more risk prudent to spend even $4.24 million or a relative percentage at your organization on preventative zero trust capabilities than to deal with the cluster of a data breach.
Take-Aways:
COVID-19 remains a catalyst for digital transformation in tech automation, IAM, big data, collaboration tools, and AI. We no longer have the same office and thus less badge access is needed. The growth and acceptability of mass WFH combined with the mass resignation/gig economy remind employers that great pay and culture alone are not enough to keep top talent. Signing bonuses and personalized treatment are likely needed. Single sign-on (SSO) will expand to personal devices and smartphones/watches. Geolocation-based authentication is here to stay with double biometrics likely. The security perimeter is now more defined by data analytics than physical/digital boundaries, and we should dashboard this with machine learning and AI tools.
Education and awareness around the review and removal of non-essential mobile apps is a top priority. Especially for mobile devices used separately or jointly for work purposes. This requires a better understanding of geolocation, QR code scanning, couponing, digital signage, in-text ads, micropayments, Bluetooth, geofencing, e-readers, HTML5, etc. A bring your own device (BYOD) policy needs to be written, followed, and updated often informed by need-to-know and role-based access (RBAC) principles. Organizations should consider forming a mobile ecosystem security committee to make sure this unique risk is not overlooked or overly merged with traditional web/IT risk. Mapping the mobile ecosystem components in detail is a must.
IT and security professionals need to realize that alleviating disinformation is about security before politics. We should not be afraid to talk about it because if we are then our organizations will stay weak and insecure and we will be plied by the same political bias that we fear confronting. As security professionals, we are patriots and defenders of wherever we live and work. We need to know what our social media baseline is across platforms. More social media training is needed as many security professionals still think it is mostly an external marketing thing. Public-to-private partnerships need to improve and app to app permissions need to be scrutinized. Enhanced privacy protections for election and voter data are needed. Everyone does not need to be a journalist, but everyone can have the common sense to identify malware-inspired fake news. We must report undue bias in big tech from an IT, compliance, media, and a security perspective.
Cloud infra will continue to grow fast creating perimeter and compliance complexity/fog. Organizations should preconfigure cloud-scale options and spend more on cloud-trained staff. They should also make sure that they are selecting more than two or three cloud providers, all separate from one another. This helps staff get cross-trained on different cloud platforms and add-ons. It also mitigates risk and makes vendors bid more competitively.
The increase in number and cost of data breaches was in part attributed to vulnerabilities in supply chains in a few national data breach incidents in 2021. Part of this was addressed in President Biden’s Executive Order 1407 on supply chain security. This reminds us to replace outdated routers, switches, repeaters, controllers, and to patch them immediately. It also reminds us to separate and limit network vendor access points to strictly what is needed and for a limited time window. Last but not least, we must have up-to-date thorough business interruption / cyber insurance with detailed knowledge of what it requires for incident response with breach vendors pre-selected.
About the Author:
Jeremy Swenson is a disruptive thinking security entrepreneur, futurist/researcher, and senior management tech risk consultant. Over 17 years he has held progressive roles at many banks, insurance companies, retailers, healthcare orgs, and even governments including being a member of the Federal Reserve Secure Payment Task Force. Organizations relish in his ability to bridge gaps and flesh out hidden risk management solutions while at the same time improving processes. He is a frequent speaker, published writer, podcaster, and even does some pro bono consulting in these areas. As a futurist, his writings on digital currency, the Target data breach, and Google combining Google + video chat with Google Hangouts video chat have been validated by many. He holds an MBA from St. Mary’s University of MN, a MSST (Master of Science in Security Technologies) degree from the University of Minnesota, and a BA in political science from the University of Wisconsin Eau Claire.
